Top Stories of the Week - 12/29

This week in the newsletter, we write about Barry Silbert resigning from Grayscale’s board, Nigeria un-banning crypto, and the creation of a new Ethereum ecosystem foundation focused on promoting decentralization.
Subscribe here and receive Galaxy's Weekly Top Stories, and more, directly to your inbox.
Silbert Out at Grayscale
Barry Silbert resigns as Grayscale board chairman. The Digital Currency Group (DCG) founder and CEO Barry Silbert, as well as DCG President Mark Murphy, have both resigned from the board of Grayscale Investments, the asset manager subsidiary of DCG. DCG’s CFO Mark Shifke, who assumed that role in July 2023, will become the new board chairman of Grayscale.
Grayscale is the largest crypto-focused asset manager in the world with $34.8bn under management as of December 27, 2023. Grayscale had applied to convert its spot-Bitcoin trust, GBTC, into an exchange traded ETF in 2021, which the SEC rejected in Summer 2022. Subsequently, Grayscale sued the SEC in the DC Circuit Court of Appeals and won in August, kicking off a firestorm of anticipation that the Commission would now eventually approve GBTC’s conversion, as well as other spot Bitcoin ETFs.
Despite the Grayscale victory, DCG has struggled over the last year following the collapse of its trading and lending subsidiary, Genesis Global. Genesis subsequently filed for bankruptcy, and Genesis, DCG, and unaffiliated New York-based firm Gemini were sued by the New York Attorney General in October of this year, with the NYAG alleging they committed fraud.
OUR TAKE:
DCG once appeared to be an unstoppable crypto conglomerate, boasting as subsidiaries the largest asset manager, largest mining pool, and largest trading business, as well as hundreds of venture portfolio companies. However, a series of bad loans made by Genesis to Three Arrows Capital and Alameda Research resulted in a large hole in the trading firm’s balance sheet, which they ultimately “plugged” with a long-term, illiquid promissory note from parent company DCG. Given that the hole was comprised of open-term liquid liabilities and the “plug” was long-term and illiquid, if further withdrawals occurred from Genesis it would be impossible for the company to remain solvent. In Fall 2022, Gemini recalled the assets it had lent to Genesis through its Gemini Earn program, forcing Genesis to declare bankruptcy. Separately, Genesis had previously lent hundreds of millions of dollars unsecured back to its parent, DCG. The ensuing bankruptcy proceedings, as well as litigation with creditors, ensnared DCG itself, putting the broader firm on shaky ground.
While shares of Grayscale fund products were often used by Genesis clients as collateral, the NYAG suit makes no allegations relating to the asset manager. The timing of Silbert’s resignation from Grayscale’s board could signal an effort to further separate the asset manager from its parent company, just as many expect the SEC to approve bitcoin ETFs, which could include the conversion of GBTC. Also worth noting is that DCG CFO Mark Shifke is a former JPM and Goldman Sachs banker with M&A experience, perhaps suggesting that Grayscale may be considering an acquisition more seriously.
Ultimately, should the SEC finally approve spot-based Bitcoin ETFs after 10 years of delays and denials, Grayscale’s court win in August will have been a major catalyzing force, for which they deserve credit. But the broader story should serve as a cautionary tale. It seems that Genesis could have survived if it had followed more conservative risk management practices and DCG would never have been in this position – a sad outcome for one of crypto’s biggest players after building a behemoth in the space for a decade and on the precipice of one of its long-held desires, a spot Bitcoin ETF. -Alex Thorn
Nigeria Lifts Three-Year Crypto Ban
Nigeria’s Central Bank lifted a three-year ban that prevented banks and other financial institutions from dealing in or facilitating transactions in crypto assets. In a circular released on December 22 entitled “Guidelines On Operations of Bank Accounts For Virtual Assets Service Providers (VASPS),” Nigeria’s central bank laid out new guidelines for financial institutions to have a banking relationship with crypto companies.
Nigeria first prohibited crypto’s use in 2021. At the time, the Central Bank cited the absence of regulations and consumer protections, as well as money laundering and terrorist financing risks, as primary reasons for the ban. Banks were forced to close accounts belonging to crypto exchanges and other businesses transacting in cryptocurrencies. Under the latest guidelines, banks and other financial institutions are still banned from holding, trading and/or transacting in virtual currencies using their own accounts, but can provide these services to VASPs licensed by the Nigerian Securities & Exchange Commission (SEC), the country’s primary markets regulator.
The new rules come more than a year after the Nigerian SEC published new digital asset regulations, the first hint that a possible regulatory change was on the way. Those rules include registration requirements for digital assets offerings and custodians and the classification of cryptocurrencies as securities. Under the newest Central Bank guidance, crypto companies that want to open a bank account will need a SEC license. Following the latest announcement, Africa’s largest crypto exchange, Yellow Card, signaled it would immediately apply for approval.
OUR TAKE:
The Nigerian government is learning that attempts to ban cryptocurrency often produce the opposite effect, inadvertently driving crypto activities further beyond their control. Despite previous bans on crypto’s use in the financial system, Nigeria has maintained a vibrant crypto ecosystem. Total crypto transaction volume grew by 9% between July 2022 and June 2023, Nigeria ranks second in Chainalysis’ 2023 Global Crypto Adoption Index, and is number one in terms of peer-to-peer exchange trade volume – an indicator meant to “highlight countries where more residents are putting a larger share of their overall income and wealth into P2P cryptocurrency transactions.” This is particularly notable given the popularity of existing peer-to-peer applications such as M-PES, which offer a more familiar and user-friendly peer-to-peer experience.
Factors such as inflation, currency controls, and periods of financial repression have led Nigerians to explore alternative stores of value and transaction methods. During protests against police brutality in 2020, for example, bitcoin was an important source of funding after organizations affiliated with the protests lost access to their bank accounts (similar usage occurred during the Canadian trucker protests in 2020). And in November Bitcoin hit an all-time-high against the Nigerian Naira following a significant devaluation of the currency.
That said, Nigeria’s newest crypto guidance is far from perfect. Banks face stringent reporting obligations which may prevent them from servicing clients. VASPs looking to establish accounts face substantial initial capital demands, including $550,000 in paid-up capital to open a bank account and a $72,000 registration fee to obtain a license from the SEC. Nigeria is also in the process of rolling out a new, government-approved stablecoin, the cNGN. These regulatory shifts could potentially give the country's major financial institutions an advantage over crypto-native entities, startups or established ones.
Decentralized digital currencies like Bitcoin are extremely resilient, popular, and global, making them almost impossible to ban. Lawmakers and regulators should learn from Nigeria’s example and better consider this resilience – rather than bans, they should devise policies that leverage the inherent benefits of crypto while effectively managing its associated risks. - Lucas Tcheyan
Introducing the PBS Foundation
On Friday, December 22, the Flashbots team,Coinbase, Consensys, Vitalik Buterin, Paradigm, the Uniswap Foundation, and Fenbushi Capital announced the creation of the PBS Foundation. The PBS Foundation is a non-profit organization based out of the Cayman Islands that will issue grants to propel research on proposer-builder separation (PBS). PBS is a design philosophy for proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchains like Ethereum that promotes the separation of validator responsibilities such as block building and proposing. By splitting up the role of a validator across more network stakeholders, the aim of PBS is to alleviate the centralizing effects of maximal extractable value (MEV). To learn more about MEV and its impact on Ethereum, read this Galaxy Research report.
The mission of the PBS Foundation is ultimately to protect the decentralization of Ethereum’s validator ecosystem through propelling research and development on PBS. Proposed by Tina Zhen, one of the cofounders of Flashbots, the Foundation will be seeded with $1m from its partners for a six-month pilot phase. Grants will be distributed across four initial topics of interest including infrastructure, research, data transparency, and community education. Notably, infrastructure grants offer funding for the creation of independent MEV relays on Ethereum that are not vertically integrated with another builder or relay. Applications for grants from the PBS Foundation can be submitted through the Foundation website here.
OUR TAKE:
MEV remains a major issue on Ethereum that contributes to the centralization of block building and transaction censorship on-chain. One of the main reasons MEV exists is due to the permissionless nature of Ethereum. The ability for anyone in the world with an internet connection and the required software to send a transaction on Ethereum creates opportunities for malicious actors to bombard the network and slow it down with spam transactions. To protect the network against denial-of-service attacks, validators, also called block proposers, have the ability to express preference over which transactions are included in a block. As financially-motivated actors, validators generally prioritize transactions according to their fee value. However, validators can also prioritize transactions according to MEV, which is the amount of money made from reordering user transactions and executing lucrative trading strategies on them such as arbitrage, frontrunning, backrunning, and sandwiching. Unlike ordering transactions by fee, earning MEV requires specialized knowledge and capital-intensive equipment from validator node operators, which over time would lead to the centralization of validator revenues to a handful of node operators.
As an initial step towards mitigating the centralizing effects of MEV on Ethereum, Ethereum core developers partnered with Flashbots to develop MEV-Boost, is a software that enables validators to connect to multiple third-party MEV marketplaces, also called relays, where they can receive pre-built blocks containing MEV. The specialized actors building lucrative blocks on behalf of validators are called “builders”. However, there is no clear solution for addressing centralization o and censorship by builders and relays. The design space for the next iteration of MEV-Boost and PBS on Ethereum is extremely expansive, as highlighted by the figure below:
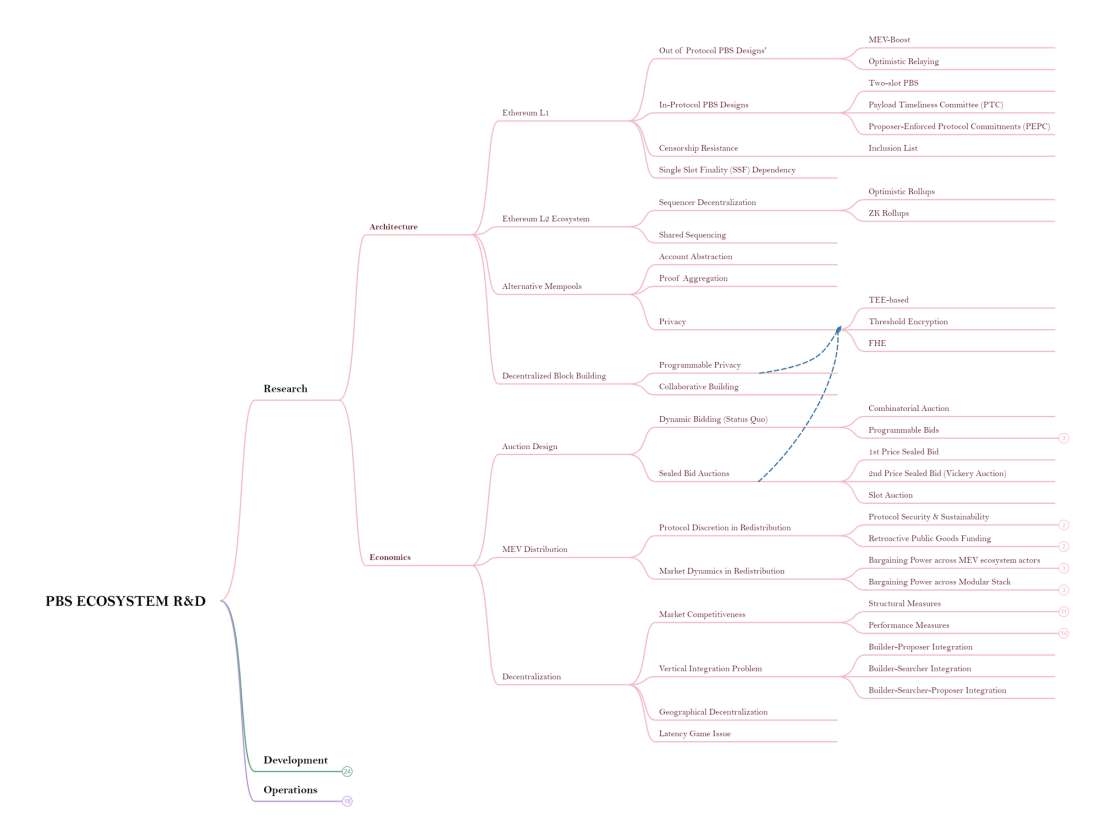
Caption: PBS Design Space
Source: PBS.salon
Given the growing complexity of the Ethereum protocol and the application ecosystem built on top, coordination across all ecosystem stakeholders from the protocol layer up is needed to address the issue of MEV. The PBS Foundation represents a concerted effort from major players in the Ethereum ecosystem to prioritize the next steps for PBS and ultimately, help propel the development of a long-term solution to the one of the most difficult problems in crypto. - Christine Kim
Charts of the Week
Thorchain and Cosmos’ Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC) have facilitated the most volume of the top cross chain platforms (e.g. bridges and cross chain swap applications). The values in the chart represent the dollar volume of digital assets transferred between chains through each platform.
Thorchain achieved $4.82bn of volume and IBC $3.35bn over the last 30 days. Arbitrum Bridge saw $1.21bn in volume over the same time, leading all other Ethereum Layer 2 (L2) bridges by at least $200m.
Other News
Hong Kong proposes licenses should be required for stablecoin issuers
Vitalik Buterin proposes three ways to make Ethereum's proof of stake design simpler
Solana non-vote transactions hit yearly high
Japan seeks to exempt companies from tax on unrealized crypto gains
BarnBridge DAO settles with SEC for $1.7 million, agrees to stop selling crypto bond product
Paxos receives approval from NY regulator to expand to Solana
Legal Disclosure:
This document, and the information contained herein, has been provided to you by Galaxy Digital Holdings LP and its affiliates (“Galaxy Digital”) solely for informational purposes. This document may not be reproduced or redistributed in whole or in part, in any format, without the express written approval of Galaxy Digital. Neither the information, nor any opinion contained in this document, constitutes an offer to buy or sell, or a solicitation of an offer to buy or sell, any advisory services, securities, futures, options or other financial instruments or to participate in any advisory services or trading strategy. Nothing contained in this document constitutes investment, legal or tax advice or is an endorsementof any of the digital assets or companies mentioned herein. You should make your own investigations and evaluations of the information herein. Any decisions based on information contained in this document are the sole responsibility of the reader. Certain statements in this document reflect Galaxy Digital’s views, estimates, opinions or predictions (which may be based on proprietary models and assumptions, including, in particular, Galaxy Digital’s views on the current and future market for certain digital assets), and there is no guarantee that these views, estimates, opinions or predictions are currently accurate or that they will be ultimately realized. To the extent these assumptions or models are not correct or circumstances change, the actual performance may vary substantially from, and be less than, the estimates included herein. None of Galaxy Digital nor any of its affiliates, shareholders, partners, members, directors, officers, management, employees or representatives makes any representation or warranty, express or implied, as to the accuracy or completeness of any of the information or any other information (whether communicated in written or oral form) transmitted or made available to you. Each of the aforementioned parties expressly disclaims any and all liability relating to or resulting from the use of this information. Certain information contained herein (including financial information) has been obtained from published and non-published sources. Such information has not been independently verified by Galaxy Digital and, Galaxy Digital, does not assume responsibility for the accuracy of such information. Affiliates of Galaxy Digital may have owned or may own investments in some of the digital assets and protocols discussed in this document. Except where otherwise indicated, the information in this document is based on matters as they exist as of the date of preparation and not as of any future date, and will not be updated or otherwise revised to reflect information that subsequently becomes available, or circumstances existing or changes occurring after the date hereof. This document provides links to other Websites that we think might be of interest to you. Please note that when you click on one of these links, you may be moving to a provider’s website that is not associated with Galaxy Digital. These linked sites and their providers are not controlled by us, and we are not responsible for the contents or the proper operation of any linked site. The inclusion of any link does not imply our endorsement or our adoption of the statements therein. We encourage you to read the terms of use and privacy statements of these linked sites as their policies may differ from ours. The foregoing does not constitute a “research report” as defined by FINRA Rule 2241 or a “debt research report” as defined by FINRA Rule 2242 and was not prepared by Galaxy Digital Partners LLC. For all inquiries, please email [email protected]. ©Copyright Galaxy Digital Holdings LP 2023. All rights reserved.




